People's Democracy
People's Democracy
(Weekly Organ of the Communist Party of
India (Marxist) No. 47
November 25,2001
(Weekly Organ of the Communist Party of
India (Marxist) |
Vol.
XXV No. 47 November 25,2001 |
The Fair Cost of Enron Equity
Prayas
INCE the last few days, newspapers have been abuzz with reports about the possible sale of the equity by foreign promoters of DPC (viz., Enron, GE and Bechtel). The preliminary termination notice issued by DPC in May 2001 expires on November 19, 2001, signalling the end of the "negotiating period". Further, the newspaper reports also indicate that the Government of India is eager to "resolve" the issue before commencement of prime minister's visit to the US. DPC's lenders, Indian and foreign, are also having hectic meetings to "resolve" this issue. All these point to the fact that the day of reckoning is not far.
INFLATED COST
In this context, the most significant issue being debated is the fair cost of DPC's equity held by the foreign promoters. Press reports indicate that Enron and the other foreign promoters are in a "benevolent mood" and are willing to forgo all profits, if they get back only what they have invested. In fact, they are talking about discounting their equity by 30 per cent, and claim that the fair price for their equity is 800 million dollars.
As against this, the prospective buyers (such as Tata and BSES) feel that this cost is too high and want the price tag to be lowered. If Enron is not prepared to accept this, the Indian financial institutions (FIs) may come under pressure to absorb the difference. This is evident in the proposals being discussed, which envisage that the FIs would buy the equity and act as the "Wear-house" for the equity, which they will sell later, absorbing the loss. The central government might also consider the option of giving tax and other concessions by declaring Dabhol as a "Mega Project". Thus, it needs to be remembered that, apart from the paying to foreign promoters, governments or FIs will have to bear the remaining losses—necessary in order to make the project viable—through the other means such as the tax losses, interest cuts, or loan write-offs.
Based on our analysis of the renegotiations committee report in 1995 (which is based on the written consent of Enron and DPC), the affidavit by the then chief minister Manohar Joshi (August 1996), and the present financing structure of the project, it could be concluded that the fair cost of equity of the foreign promoters is not more than 320 million dollars (Rs 1,500 crore). This too is based on the condition that DPC completes the project to make it ready for power generation in the next six months, without burdening the project with any additional loans.
REVIVAL OF THE PROJECT
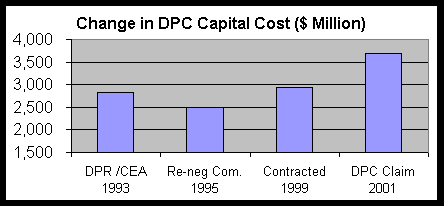
Let us start with what Enron promised in the Detail Project Report (DPR) submitted to the CEA in 1993. In this, Enron claimed a capital cost of US 2,828 million dollars. CEA is said to have approved this capital cost. Subsequent to this purported clearance, Enron went ahead and started construction of the Phase I of the project. In 1995, the BJP-Sena government cancelled the project, following the Munde Committee report. Later, in less than six months, the entire project including Phase II was revived by the same government following the recommendations of the "Renegotiations Committee". The government boasted that the primary reason for revival of the project was substantial reduction in the capital cost to US 2,500 million dollars (from 2,828 million dollars). This reduction in capital cost was claimed as one of the significant factors for revival of the project by the then chief minister (Manohar Joshi) in his affidavit (dated August 30, 1996) in the Bombay High Court.
Further, it is essential to note that, on page 3 of the "re-negotiation" committee's report, it is clearly mentioned that "Enron and DPC representatives have given their written consent," inter alia, to reduce the capital cost of the project to US 2,500 million dollars.
ACTUAL EQUITY COMPONENT
But as is known by now, by 1999, DPC had already borrowed a total loan (from Indian and foreign institutions) of nearly 2,050 million dollars for the project. This implies that the total equity component of the project is only 450 million dollars (2,500 million dollars minus 2,050 million dollars). Out of this equity, the MSEB has already put in 130 million dollars as its own equity. So, the total equity that is required to be put in by the foreign promoters is barely 320 million dollars. As the project stands today, it is no different from the project that was renegotiated. Enron, DPC and government of Maharashtra all have agreed in writing for this capital cost.
Further, on several occasions, Enron has guaranteed completion of the project within the agreed cost. Hence, any claim of foreign promoters' equity which is more than this amount is completely unjustified and hence need not be entertained. In other words, purchase of entire equity of all foreign promoters for a price more than 320 million dollars (Rs 1,500 crore) would amount to a paying a premium to Enron and not discount.
On this background, Enron's demand for 800 million dollars while claiming to offer a discount of 30 per cent, is nothing but an attempt to burden the buyer of the equity and or the consumers in Maharashtra for Enron's own inefficiency.
Just a few months ago, i.e., before the work on the project was suspended owing to the disputes between MSEB and DPC, the latter had said that the project cost had escalated and it would complete the project at a cost of 3,326 million dollars ! This astonishing cost over-run of 826 million dollars (or 33 per cent of project cost) is the result of nothing but Enron's inefficiency. Enron's claim of selling equity at 800 million dollars (which is said to be at a 30 per cent discount) makes sense only if this entire inefficiency (cost overrun) is to be funded through equity and is considered legitimate and justifiable.
But, the story does not end here, and Enron (as usual) wants more and more. Few months before the suspension of work, it was claimed that over 90 per cent of the project work was complete. But due to just a few months suspension of the work, now Enron is claiming the additional cost of US 360 million dollars, i.e., 14 per cent additional cost overrun for completion of the project ! So, now Enron is claiming a project cost of 3,690 million dollars instead of 2,500 million dollars — a difference of 1,190 million dollars (or a cost increase of Rs 5,500 crore).
RELATED ISSUES
Any effort to salvage the project would imply a change in the PPA. This will necessitate an approval of the regulatory commission (RC) for the entire PPA. Unlike the earlier processes, the regulatory process would be transparent. RC is bound to make public, all the project related contracts, seek public objections, have public hearings and give a reasoned order. Apart from the issues mentioned above, several other issues are bound to come up during this process. (For example, the applicability of recent availability based tariff prescribed by CERC would be debated.) Similarly, the reasonability of even the 2,500 million dollars project cost — which means 919 dollars per kw (excluding LNG terminal costs)—would be questioned. It is worth remembering that this per kw cost of DPC is too high against the international norm of 600 dollars /kw for similar projects. Hence, if the total project cost goes beyond the mutually consented figure of 2500 million dollars, then it is bound to be challenged before the RC and will probably be disallowed. This will force the relevant party—most probably the government or the financial institutions — to absorb this additional payment as its loss. In such a situation, the premium paid to Enron will be funded through the hard earn money of the tax-payers or investors, which would be, to say the least, scandalous.
Thus, it is yet to be decided, as to who will bear the burden of the excess cost of this sweet-heart deal — Enron, the prospective buyer (i.e., their shareholders), the consumers, the Indian financial institutions (i.e., the investors), or the government (i.e., the tax-payers).
Note: Prayas is an energy NGO in Pune, which has worked extensively on Enron and its PPA.
Table 1 :
Story of DPC Capital Costs (figures in million dollars)
DPR /CEA |
Re-neg Com. |
Contracted |
Additional claim |
||
1993 |
1995 |
1999 |
2001 |
||
1 |
Power Plant, spares etc |
1,343 |
1,189 |
1,430 |
- |
2 |
LNG terminal |
370 |
335 |
484 |
- |
3 |
DPC Costs & Contingencies |
223 |
217 |
200 |
- |
4 |
Financing Costs |
72 |
106 |
205 |
- |
5 |
Taxes and Duties |
369 |
221 |
164 |
- |
6 |
IDC, Working Capital, Insurance |
451 |
434 |
463 |
- |
Total |
2,828 |
2,501 |
2,946 |
- |
|
1 |
Cost Over-run |
268 |
|||
2 |
Unpaid - Taxes |
112 |
|||
3 |
Suspension cost |
360 |
|||
DPC Claimed Costs |
3,686 |